Chapter 6 - Nervous Tissue
Questions are provided for the most important slides of this chapter. This quiz only covers material that one would be expected to discuss in a histology laboratory.
Nervous tissue is composed of two major types of cells? [+]
- Neurons - structural and functional unit of the nervous system
- Neuroglia (or glial cells) - supporting cells for neurons
Nervous system is divided anatomically into two major components: [+]
- Central nervous system (CNS) – consists of the brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – all nervous tissue outside the CNS
Name the three parts of a neuron and their functions: [+]
- Cell body (or perikaryon, soma) – processes and integrates signals from dendrites
- Dendrites – branched processes that receive stimuli and conduct impulses toward the cell body
- Axon – single axon that conducts nerve impulses to other cells through synapses
Three structural classifications of neurons based on their processes: [+]
- Bipolar - found in special sensory organs, like olfactory and vision
- Pseudounipolar (or unipolar) - sensory neurons found in dorsal root (or spinal) ganglia
- Multipolar - most common type of neuron
Part 01
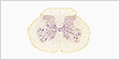
Name the four types of glial cells in the CNS and their functions: [+]
- Astrocytes – many roles in support and nourishment of neurons
- Oligodendrocytes – insulate axons and form myelin sheaths around more than axon
- Microglia – specialized macrophages
- Ependymal cells – line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord - produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
 |
|
 |
Part 02
What is a cluster of nerve cell bodies outside the CNS called? [+]
What is another name for neurons with cell bodies in ganglia? [+]
Name the two types of glial cells in the PNS: [+]
- Schwann cells – structure depends whether the axons are unmyelinated/myelinated
- Wrap multiple, unmyelinated axons in cytoplasmic folds
- Wrap a single, myelinated axon within a myelin sheath
- Satellite (or capsule) cells – cells that support neurons in ganglia
 |
Part 03
Autonomic nervous system is divided into two subdivisions: [+]
- Sympathetic nervous system – involved in functions requiring quick responses (i.e., stress, impending danger, and "fight or flight" response)
- Parasympathetic nervous system – regulates functions of body organs, blood vessels, and smooth muscle (i.e., "rest and digest" response)
How can you differentiate sympathetic ganglia from parasympathetic ganglia? [+]
 |
|
 |
Part 04
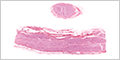
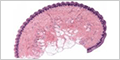
Bundles of axons in the PNS that extend to and from the CNS? [+]
 |
|
 |