Chapter 13 - Endocrine Glands
Endocrine glands secrete their hormones into the blood where they are transported to other tissues where they interact with receptors on target cells and alter their function.
Thyroid
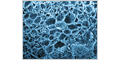
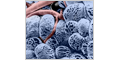
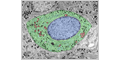
The thyroid secrets thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine and tetraiodothyronine) that increase oxygen consumption and metabolic rates of most tissues.
 |
|
 |
Adrenal
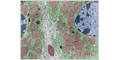
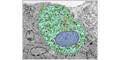
The adrenal glands are found above the kidneys. The adrenal cortex is divided into three zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticulars. They produce a variety of hormones including adrenline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol.
 |
|
 |
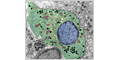
Pituitary
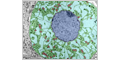
The pituitary gland is often called the master gland because it controls several other hormone glands in your body, including the thyroid and adrenals, the ovaries and testicles.
Most cell types can be distinguished by the differences in morphology of their secretion granules. (More easily done by using immunohistochemistry with antibodies to different hormones.)
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |