Chapter 9 - Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system transports blood to and from tissues. It consists of a pump (heart), vessels to deliver blood to tissues (arteries), network of vessels to perfuse tissues (capillaries) and vessels to return blood to the heart (veins).
HEART
The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
BLOOD VESSELS
Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body. Arteries, arterioles, and capillaries carry blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
CAPILLARIES
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are responsible for the exchange of gases, nutrients and other substances between blood and tissues.
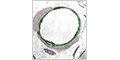
Continuous Capillaries
Continuous capillaries completely enclose the lumen of the blood vessel. Typically found in muscle, nerve and connective tissue.
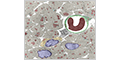 |
Pericytes are mesenchymal cells with long cytoplasmic processes that partly wrap around continuous capillaries. They are involved in blood flow, blood-brain barrier, angiogenesis and muscle regeneration.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
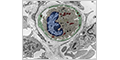
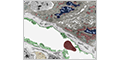
Fenestrated Capillaries
Fenestrated capillaries contain numerous small pores (or fenestrations) that make them far more permeable than continuous capillaries. Typically found in in tissues involved in absorption (gastrointestinal tract, kidney and gallbladder) and endocrine glands.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Sinusoidal Capillaries
Sinusoidal capillaries are larger than other capillaries and have a discontinuous endothelium. This allows easier movement of cells between the blood and tissues. Their found in the liver, lymphoid tisse, endocrine glands, and hematopoietic organs.
 |
 |
 |