Chapter 2 - Epithelium
Epithelia are sheets of cells that cover the external surface and line the internal surfaces of the body. They are classified by:
- Shape of the surface cells
- Whether it has a single or multiple layers of cells
 |
All epithelia make a basement membrane that forms a boundary between it and the underlying connective tissue.
Epithelia are polarized:
- Apical surface- parts of cells or those cells next to the free surface or lumen
- Basal surface - parts of cells or those cells next to the basement membrane
- Lateral surfaces - parts of cells adherent to the sides of adjacent epithelial cells
It is not necessary to learn the names of specific tissues for this chapter, but rather learn to recognize variations in epithelia.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flattened cells. It often occurs at sites of metabolite, fluid or gas exchange across or between cells.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
A simple cuboidal epithelium consists of a single layer of cells of similar height and width. Limited distribution but often found in the lining of ducts.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Simple Columnar Epithelium
A single columnar epithelium consists of a single layer of cells that are taller than they are wide. Typically associated with secretion or absorption.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
A pseudostratified columnar epithelium appears stratified because:
- Some cells do not reach the apical surface
- All cells rest on the basement membrane
- Nuclei are at different levels
- Cells appear tightly packed
Therefore, it is a specialized type of a simple columnar epithelium. It lines the upper respiratory tract.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
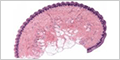
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium has two or more layers of cells. Only the basal layer of cells rests on the basement membrane. Its name arises from the squamous appearance of the surface layer of cells. The epithelium is keratinized on the external surface of the body to prevent loss of water and protect against abrasion.
 |
(keratinized and non-keratinized) |
 |
(non-keratinized) |
 |
(non-keratinized) |
 |
(keratinized) |
 |
(keratinized) |
 |
(keratinized) |
 |
(non-keratinized) |
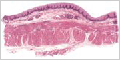
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
A stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of two or more layers of cells. Only the cells of the surface layer are cuboidal with subsequent layers varying in shape from cuboidal to polyhedral. Limited distribution found only in the lining of larger ducts.
 |
|
 |
Transitional Epithelium
A transitional epithelium consists of multiple layers of cells. The surface layer is composed of much larger, dome-shaped cells (umbrella cells) that change in shape when the epithelium is relaxed or stretched. Found only in the urinary tract.
 |
(relaxed and stretched bladder) |
 |