Chapter 6 - Nervous Tissue
The nervous system is specialized for communication of information from one region of the body to another.
Nervous system is divided anatomically into two major components:
- Central nervous system (CNS) – consists of the brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – all nervous tissue outside the CNS
Nervous system is divided functionally into two major components:
- Somatic nervous system – conscious voluntary movements
- Autonomic nervous system – regulates the functions of internal organs - further divided into two subdivisions:
- Sympathetic nervous system – involved in functions requiring quick responses (i.e., stress, impending danger, and fight or flight response)
- Parasympathetic nervous system – regulates functions that do not require a quick response
Although the CNS will be briefly examined, most of the emphasize wil be on the PNS.
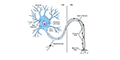
NEURON
The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. However, non-neural cells (i.e., glial cells) provide support and protection in the CNS (oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia) and the PNS (Schwann cells and satellite cells).
 |
|
 |
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Brain
Neurons have considerable variation in their size and shape. Because of the large size of human brains, the smaller rat brain is examined here.
 |
(Golgi's Stain) |
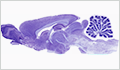 |
(Nissl/Chromophil Substance) |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals between the brain and the body.
 |
|
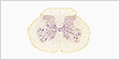 |
(Nissl/Chromophil Substance) |
 |
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists all nervous tissue outside of the central nervous system.
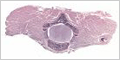
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Dorsal root ganglia are clusters of nerve bodies of sensory neurons located alongside the spinal cord.
 |
|
 |
MHS 285-286 Dorsal Root Ganglion (toluidine blue / myelin stain) |
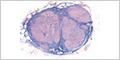 |
(azan) |
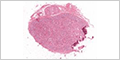 |
Sympathetic Ganglion
Sympathetic ganglia form long chains on either side of the spinal cord. They deliver information about stress, impending danger, and the fight-or-flight response.
 |
|
 |
Parasympathetic Ganglion
Parasympathetic nerves have their nerve cell bodies in small ganglia located within the organ they innervate.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Peripheral Nerve
Peripheral nerves contain the axons of both motor neurons and sensory neurons that connect with the spinal cord. They are surrounded by multiple layers of connective tissue.
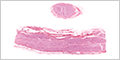 |
(longitudinal and cross sections) |
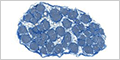 |
(Masson's trichrome) |
 |
Sensory Nerve Endings
The nervous system has a variety of specialized receptors. Meissner's and Pacinian corpuscles are two that can be readily seen by H&E.
 |
(Meissner's and Pacinian corpuscles) |
 |
(Meissner's corpuscle) |
 |
(Pacinian corpuscle) |