Chapter 9 - Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system transports blood to and from tissues. It consists of a pump (heart), vessels to deliver blood to tissues (arteries), network of vessels to perfuse tissues (capillaries) and vessels to return blood to the heart (veins).
HEART
Human heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The work load of the ventricles is much larger and its wall thickness is much greater than the atria.
Cardiac muscle is striated, involuntary muscle found in the heart wall.
 |
(right and left atria) |
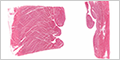 |
(right and left ventricles) |
 |
Heart Valves and Cardiac Skeleton
The cardiac skelton is dense connective tissue that fibrous rings that surround and support the cardiac valves.
Purkinje Fibers
Purkinje fibers are specialized muscle fibers that relay impulses to create synchronized contractions of the ventricles.
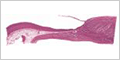 |
(H&E / phosphotungstic acid) |
 |
(periodic-acid Schiff's stain) |
 |
BLOOD CIRCULATION
The circulatory system transports blood to and from tissues. It consists of vessels to deliver blood from the heart to tissues (arteries), network of vessels to perfuse tissues (capillaries) and vessels to return blood to the heart (veins).
 |
Elastic Artery and Large Vein
Elastic arteries (arota, carotid, subclavian and lilac arteries) have two functions: conduction of a large volume of lood and maintenance of blood pressure during diastole.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
MH 065-066 Aorta and Vena Cava (H&E / Verhoeff) |
 |
(H&E) |
Muscular Artery and Medium Vien
Muscular arteries cover a wide range of sizes and regulate the distribution of blood various regions of the body.
 |
(H&E / Verhoeff / azan) |
 |
MH 061-062 Popliteal Artery and Vein (H&E / Verhoeff) |
 |
|
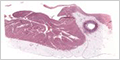 |
(coronary artery) |
Arterioles and Venules
Arterioles are the smallest category of arteries which have a role in maintaining blood pressure.
 |
(H&E / Verhoeff) |
Microvasculature
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are responsible for the exchange of gases, nutrients and other substances between blood and tissues.
 |
(capillaries) |
Sinusoidal capillaries are larger than other capillaries and have a discontinuous endothelium. This allows easier movement of cells between the blood and tissues.
 |
(sinusoidal capillaries) |
Capillary beds can be seen in whole mounts of tissues.
 |
MH 060 Microvasculature (mesentery) (silver) |
Venous Valve
Medium and large veins have valves that prevent retrograde flow of blood.
 |
Damage to the Femoral Artery
Atherosclerosis can result from injury to the tunica intima by chemicals in the blood, hypertension, and bacterial or viral infections. This damage results in the thickening of the tunica intima.
 |